1 Introduction
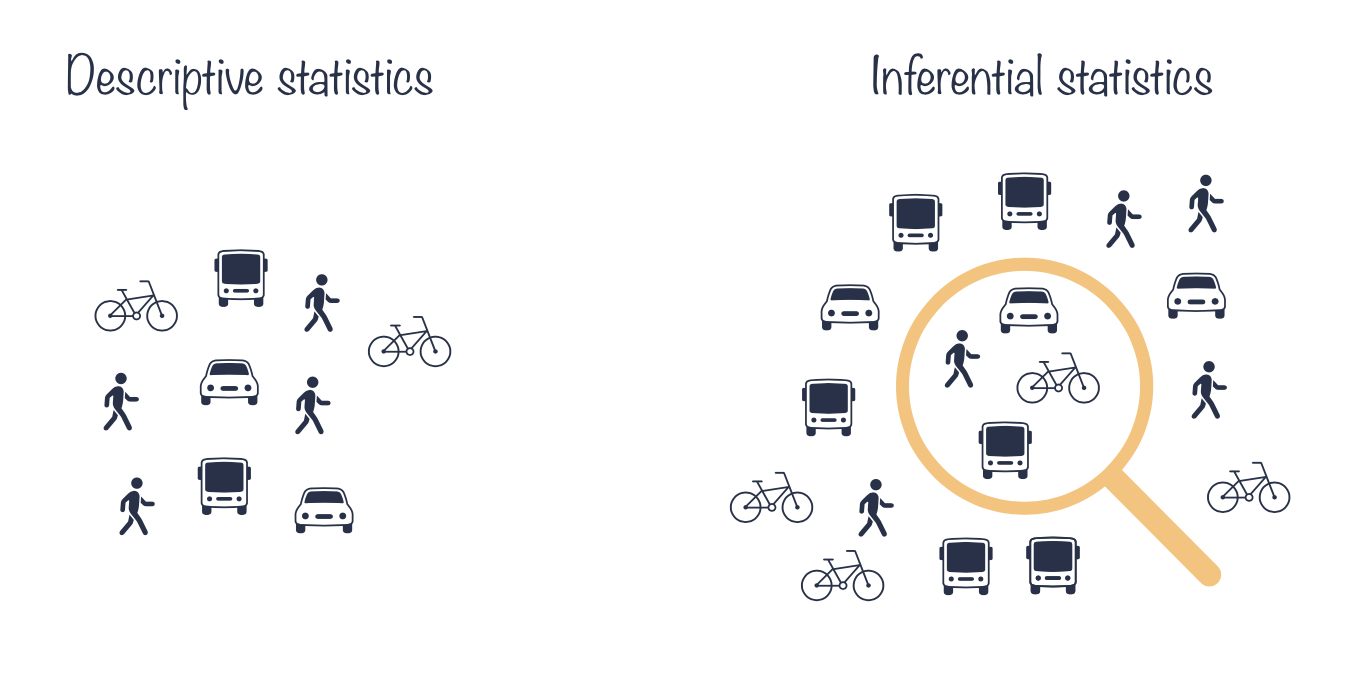
Statistics is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. Two main types of statistics are descriptive and inferential statistics. Descriptive statistics describes and summarizes the data (sample) whereas inferential statistics uses a sample of data to learn about the population that the sample of data is thought to represent.
Using descriptive statistics we can say for example that 40% of our research group members usually walk to work, 20% cycle, 20% take a bus and 20% drive. Assuming our research group is a representative sample of larger population of research groups, using statistical inference we can ask and answer questions such as what percentage of researches usually drive to work?
Descriptive statistics
In other words, a descriptive statistic is a summary statistics that quantitatively describes features of collected information, e.g. percentage of our research group who walked to work on Monday. Descriptive statistics uses and analyses these statistics to help us to understand the data by:
- describing the data
- visualizing the data
- summarizing the data
Descriptive statistics is also used to:
- uncover potential patterns in the data including outliers
- and guide down-stream analysis