{
"R": {
"Version": "4.3.2",
"Repositories": [
{
"Name": "CRAN",
"URL": "https://p3m.dev/cran/latest"
}
]
},
"Bioconductor": {
"Version": "3.18"
},
"remotes": {
"Package": "remotes",
"Version": "2.4.2.1",
"Source": "Repository",
"Repository": "RSPM",
"Requirements": [
"R",
"methods",
"stats",
"tools",
"utils"
],
"Hash": "63d15047eb239f95160112bcadc4fcb9"
}
}Renv: Project environments in R
RaukR 2024 • Advanced R for Bioinformatics
Roy Francis
21-Jun-2024
Terminology
R package
- A standardized collection of R code, data or documentation
- How you use someone else’s code
installed.packages()
R library
- A directory that holds R packages
- Where you store packages
.libPaths()
R repository
- A server that hosts R packages for distribution
- Where you get packages from
getOption("repos")
Motivation
Unable to reproduce the same results when
- Rerunning old code
- Sharing your code with others
Can you answer these questions about your project?
- Where did I get my package from? What’s my repository?
- Where is my package stored? Where is my package library?
- What version of the package did I use?
renv is a toolkit to manage project-specific libraries of R packages

What can renv do?
Isolate projects
- Each project gets it’s own library
- You can use different versions of a library in different projects
Reproducible
- Record exact version of each package
Portable
- You or others can restore the project libraries with the same exact versions
- And from the same repository as you did
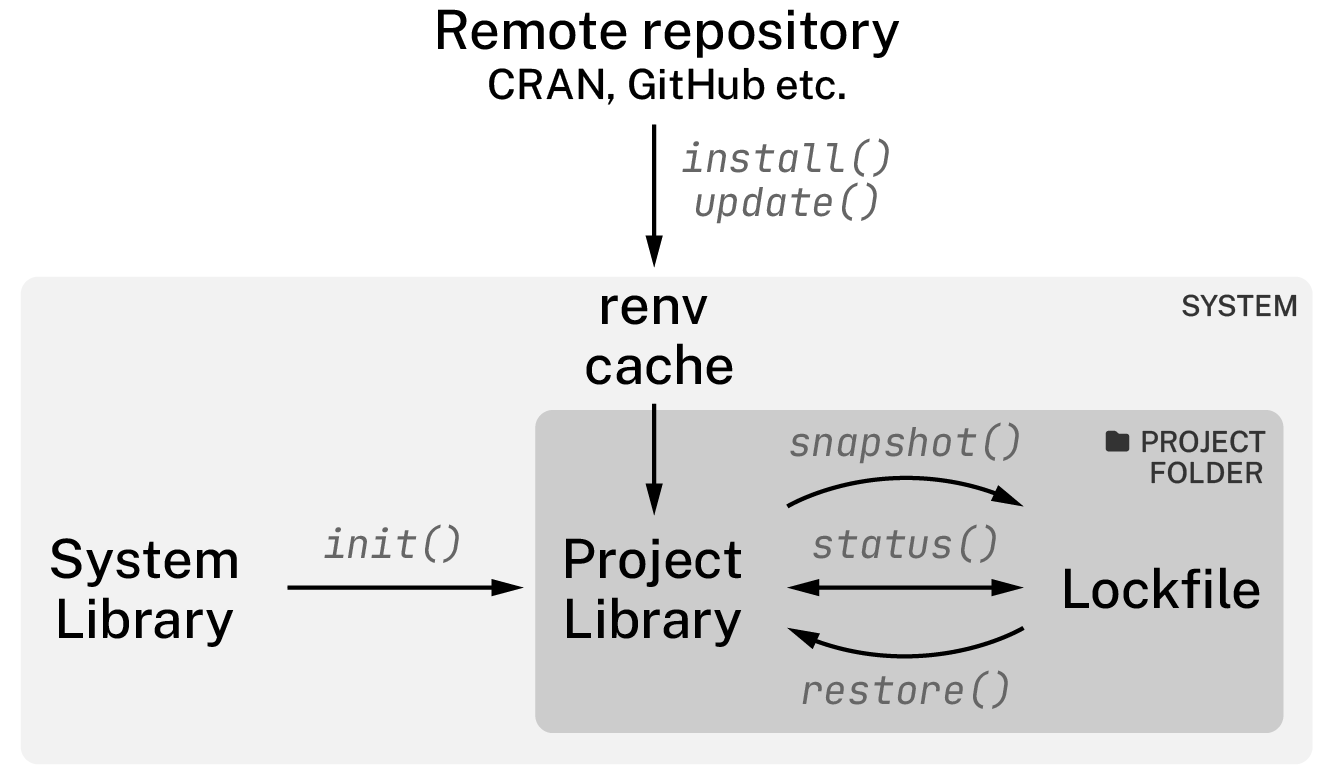
renv workflow
Initialize
renv::init()Write code install packages
install.packages()Record environment
renv::snapshot()Repeat 2 & 3
Restore environment if needed
renv::restore()
Initialize
> renv::init()
renv: Project Environments for R
Welcome to renv! It looks like this is your first time using renv.
This is a one-time message, briefly describing some of renv's functionality.
renv will write to files within the active project folder, including:
- A folder 'renv' in the project directory, and
- A lockfile called 'renv.lock' in the project directory.
In particular, projects using renv will normally use a private, per-project
R library, in which new packages will be installed. This project library is
isolated from other R libraries on your system.
In addition, renv will update files within your project directory, including:
- .gitignore
- .Rbuildignore
- .Rprofile
Finally, renv maintains a local cache of data on the filesystem, located at:
- "~/Library/Caches/org.R-project.R/R/renv"
This path can be customized: please see the documentation in `?renv::paths`.
Please read the introduction vignette with `vignette("renv")` for more information.
You can browse the package documentation online at https://rstudio.github.io/renv/.
Do you want to proceed? [y/N]: y
- "~/Library/Caches/org.R-project.R/R/renv" has been created.
- Linking packages into the project library ... [32/32] Done!
The following package(s) will be updated in the lockfile:
# CRAN -----------------------------------------------------------------------
- R6 [* -> 2.5.1]
- base64enc [* -> 0.1-3]
- bslib [* -> 0.6.1]
- cachem [* -> 1.0.8]
- fastmap [* -> 1.1.1]
- rmarkdown [* -> 2.25]
- sass [* -> 0.4.8]
- vctrs [* -> 0.6.5]
- xfun [* -> 0.41]
- yaml [* -> 2.3.8]
The version of R recorded in the lockfile will be updated:
- R [* -> 4.3.2]
- Lockfile written to "~/Downloads/test/renv.lock".
- renv activated -- please restart the R session.Status
What has changed in my project compared to the previous record?
> renv::status()
The following package(s) are missing:
package installed recorded used
dplyr n n y
ggplot2 n n y
shiny n n y
See ?renv::status() for advice on resolving these issues.Snapshot
> renv::snapshot()
The following required packages are not installed:
- dplyr
- ggplot2
- shiny
Packages must first be installed before renv can snapshot them.
Use `renv::dependencies()` to see where this package is used in your project.
What do you want to do?
1: Snapshot, just using the currently installed packages.
2: Install the packages, then snapshot.
3: Cancel, and resolve the situation on your own.> renv::snapshot()
The following package(s) will be updated in the lockfile:
# RSPM -----------------------------------------------------------------------
- dplyr [* -> 1.1.4]
- fansi [* -> 1.0.6]
- generics [* -> 0.1.3]
- tidyselect [* -> 1.2.0]
- utf8 [* -> 1.2.4]
- withr [* -> 3.0.0]
Do you want to proceed? [Y/n]:renv workflow
# record current state of packages
renv::snapshot()renv.lock anatomy
renv.lock anatomy • R version
{
"R": {
"Version": "4.3.2",
"Repositories": [
{
"Name": "CRAN",
"URL": "https://p3m.dev/cran/latest"
}
]
},
"Bioconductor": {
"Version": "3.18"
},
"remotes": {
"Package": "remotes",
"Version": "2.4.2.1",
"Source": "Repository",
"Repository": "RSPM",
"Requirements": [
"R",
"methods",
"stats",
"tools",
"utils"
],
"Hash": "63d15047eb239f95160112bcadc4fcb9"
}
}renv.lock anatomy • Active repositories
{
"R": {
"Version": "4.3.2",
"Repositories": [
{
"Name": "CRAN",
"URL": "https://p3m.dev/cran/latest"
}
]
},
"Bioconductor": {
"Version": "3.18"
},
"remotes": {
"Package": "remotes",
"Version": "2.4.2.1",
"Source": "Repository",
"Repository": "RSPM",
"Requirements": [
"R",
"methods",
"stats",
"tools",
"utils"
],
"Hash": "63d15047eb239f95160112bcadc4fcb9"
}
}renv.lock anatomy • R packages
{
"R": {
"Version": "4.3.2",
"Repositories": [
{
"Name": "CRAN",
"URL": "https://p3m.dev/cran/latest"
}
]
},
"Bioconductor": {
"Version": "3.18"
},
"remotes": {
"Package": "remotes",
"Version": "2.4.2.1",
"Source": "Repository",
"Repository": "RSPM",
"Requirements": [
"R",
"methods",
"stats",
"tools",
"utils"
],
"Hash": "63d15047eb239f95160112bcadc4fcb9"
}
}Package metadata
- Package: Package name
- Version: Package version
- Source: Source location
- Repository: Name of repository
- Hash: Unique hash for this package
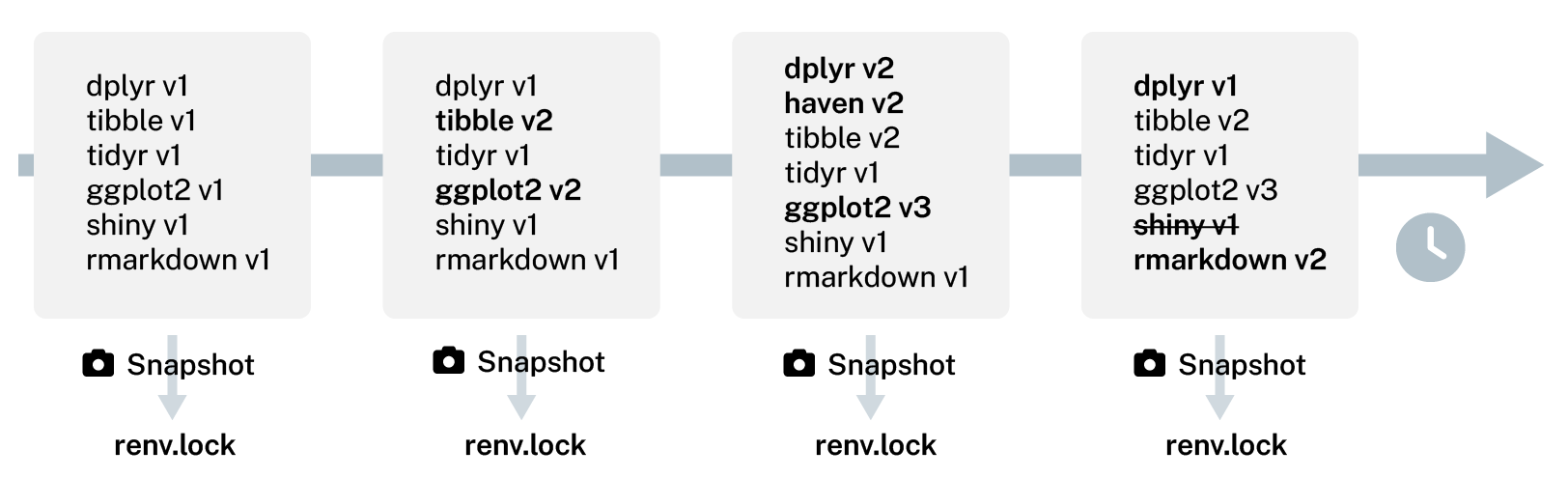
Practical use cases for lockfile
- Time capsules: Freeze exact versions of packages for future
- Collaborate using the same library
- Deploy development environment to a remote server
Restoring library
> renv::restore()
The following package(s) will be updated:
# CRAN -----------------------------------------------------------------------
- R6 [* -> 2.5.1]
- fontawesome [* -> 0.5.2]
- xfun [* -> 0.41]
- yaml [* -> 2.3.8]
# RSPM -----------------------------------------------------------------------
- dplyr [* -> 1.1.4]
- fansi [* -> 1.0.6]
- withr [* -> 3.0.0]
Do you want to proceed? [Y/n]:renv::restore()- Rebuild a project library from a lockfile
- Handles multiple sources
- CRAN
- Bioconductor
- GitHub
- Gitlab
- Bitbucket
- Private repositories…
- Will not modify R version
Tracking renv.lock
# view lockfile history
renv::history()
# revert to previous state
renv::revert(commit="commit 2")How renv works
Without renv
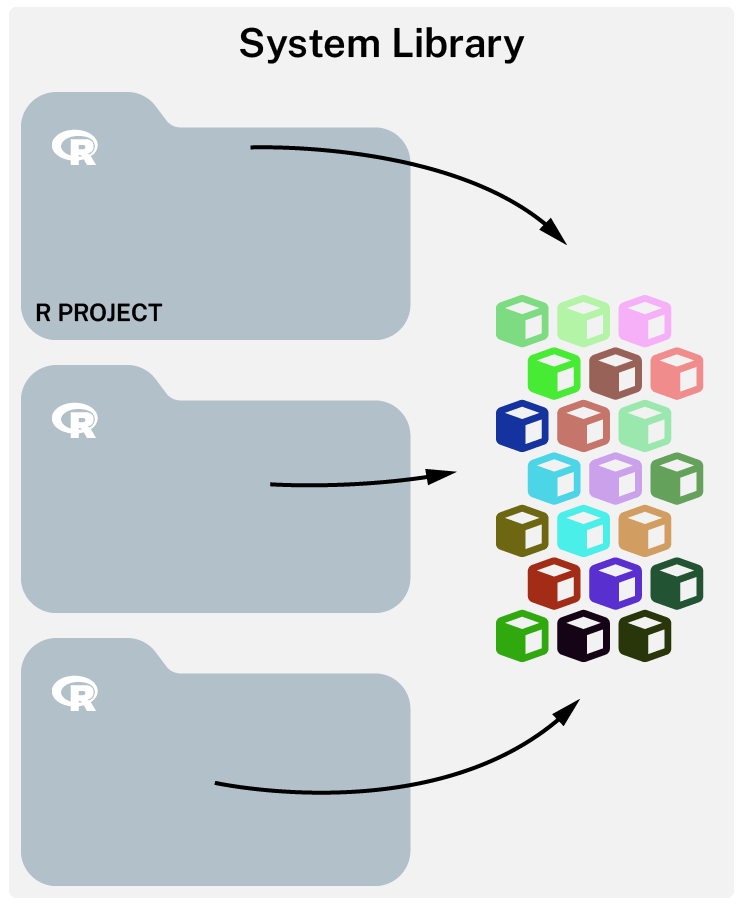
- All projects share the same library
- Changes in one project affects the other
How renv works
Project specific library without global cache

- Each project has it’s own library
renv::settings$use.cache(FALSE)disables global cache
How renv works
Project specific library with global cache
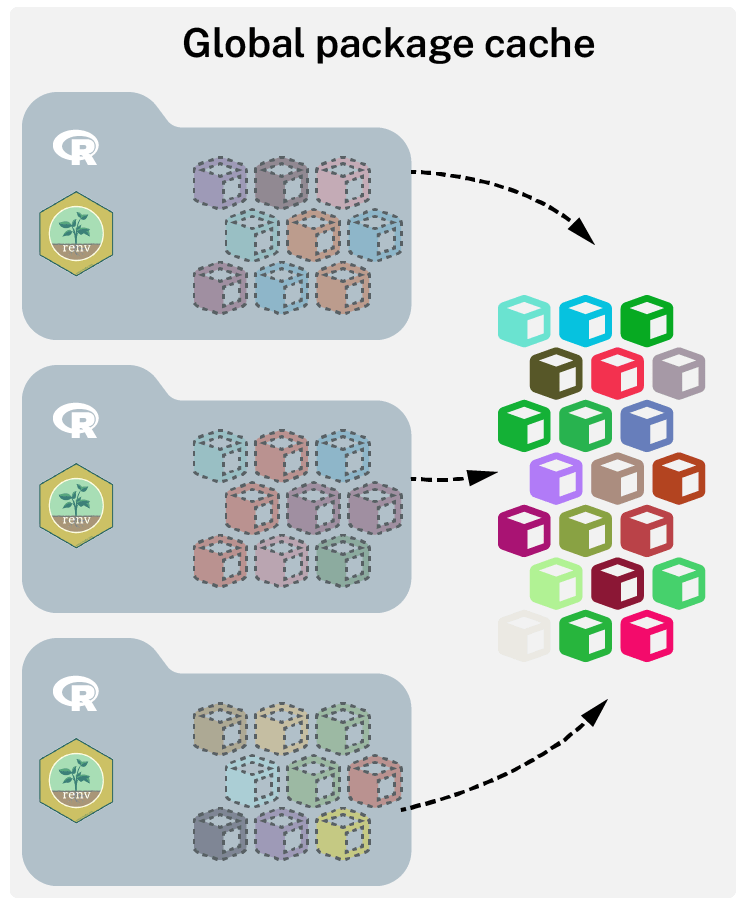
- Each project has it’s own library
- Projects libraries are soft-linked to global cache
| OS | Location |
|---|---|
| Linux | ~/.local/share/env |
| MacOS | ~/Library/Application Support/renv |
| Windows | %LOCALAPPDATA%/renv |
RENV_PATHS_CACHE Set this environment variable to share package cache across multiple users
Project profiles
- Switch between different profiles
- By default, the “default” profile is used
- Create or switch profiles
renv::activate(profile = "dev")
Install packages using renv
> renv::install(c("dplyr"))
# Downloading packages -------------------------------------------------------
- Downloading dplyr from CRAN ... OK [file is up to date]
- Downloading generics from CRAN ... OK [file is up to date]
- Downloading pillar from CRAN ... OK [file is up to date]
- Downloading fansi from CRAN ... OK [file is up to date]
- Downloading utf8 from CRAN ... OK [file is up to date]
- Downloading tibble from CRAN ... OK [file is up to date]
- Downloading pkgconfig from CRAN ... OK [file is up to date]
- Downloading tidyselect from CRAN ... OK [file is up to date]
- Downloading withr from CRAN ... OK [file is up to date]
Successfully downloaded 9 packages in 5.8 seconds.
The following package(s) will be installed:
- dplyr [1.1.4]
- fansi [1.0.6]
- generics [0.1.3]
- pillar [1.9.0]
- pkgconfig [2.0.3]
- tibble [3.2.1]
- tidyselect [1.2.0]
- utf8 [1.2.4]
- withr [3.0.0]
These packages will be installed into "~/Downloads/test/renv/library/R-4.3/x86_64-apple-darwin13.4.0".
Do you want to proceed? [Y/n]:Tidbits
- Implicit snapshotting
- Only packages which appear to be used in the project is recorded
renv::snapshot()
- Snapshot all packages in current library regardless of project
renv::snapshot(type="all")
- Discover dependencies manually
renv::dependencies()
- Explicit snapshotting
- Only record packages specified in DESCRIPTION file
renv::settings$snapshot.type("explicit")
- Ignore a package explicitly
renv::settings$ignored.packages("<package>")
Tidbits
- Restore into system library
renv::restore()
- Disable global cache
renv::settings$use.cache(FALSE)
- Install to global cache
renv::install()
- Update packges to newer versions
renv::update()
- renv is integrated into RStudio projects (.Rproj)
- Disable renv
- Temporary deactivate renv
renv::deactivate()renv::activate()
- Remove renv from current project (removes renv/, renv.lockfile, .Rprofile)
renv::deactivate(clean=TRUE)
- Remove renv global cache
unlink(renv::paths$root(), recursive=TRUE)
- Temporary deactivate renv
Renv is only one piece of the reproducibility puzzle

Renv is only one piece of the reproducibility puzzle
Renv is only one piece of the reproducibility puzzle
Renv is only one piece of the reproducibility puzzle
Renv is only one piece of the reproducibility puzzle
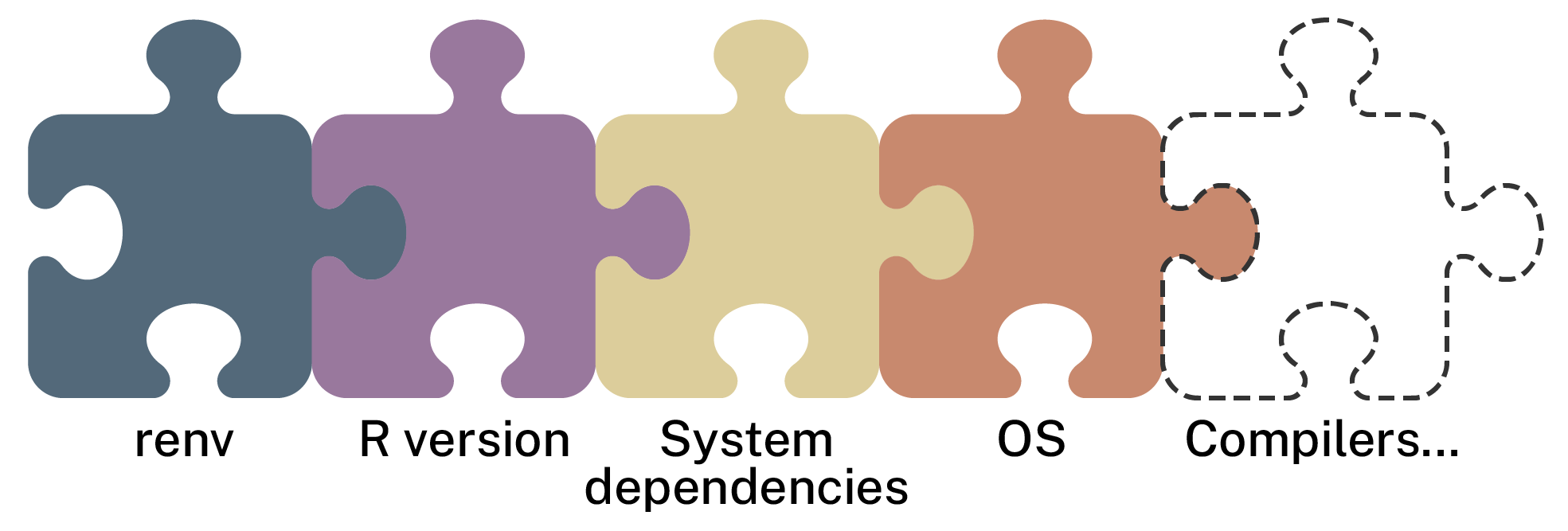

Recap
Key functions
renv::init()
renv::snapshot()
renv::restore()Useful
renv::status()
renv::dependencies()
renv::history()
renv::revert()
Acknowledgements
Project environments for R, Kevin Ushey, RStudio::Conf 2020
Reproducible environments with renv, Ryan Johnson, NHS-R community 2023
renv official documentation
Thank you! Questions?
_
platform x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
os linux-gnu
major 4
minor 3.2 2024 • SciLifeLab • NBIS • RaukR