Gene set analysis
Single Cell RNA-Seq Analysis
Jennifer Fransson
02-Apr-2025
What is gene set analysis?
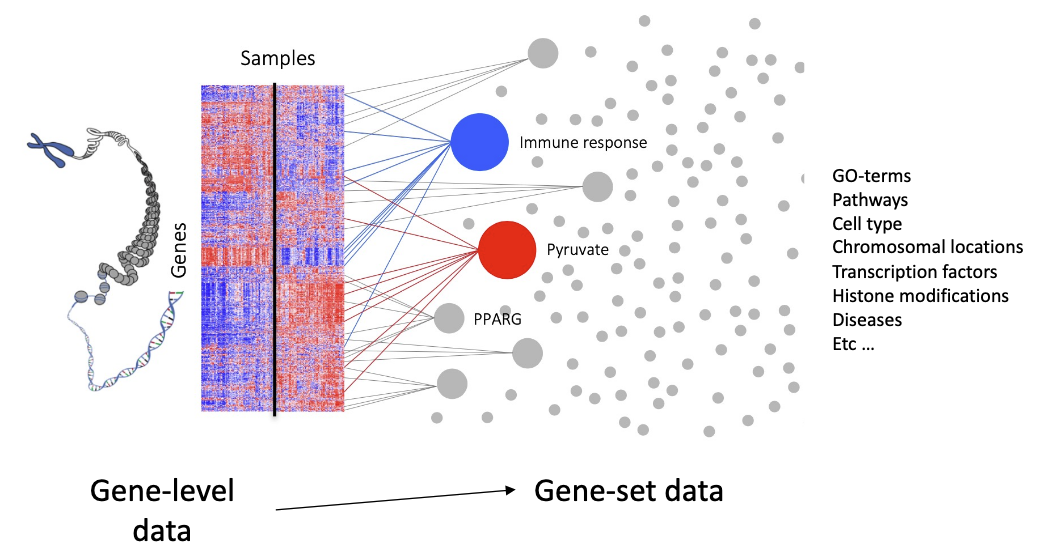
Gene-level data -> Gene set data
We focus on transcriptomics and DGE, but in principle applies to any genome-wide data
Why gene set analysis?
Predict the functional changes of cells based on differential gene expression analysis
- Make sense of a long list of DEGs
- What is the function of those genes?
- What is the biological consequence of over/under expression of genes?
- Connect your DEGs and thereby your experiment to pathway activity
- Small differences in many genes may have a bigger impact than large differences in one genes
- Less sensitive to false positive DEGs
Requirements
DE results
+
Gene set(s) (list(s) of genes)
+
Statistical test
Where to get gene sets?
- Databases
- Gene Ontology
- KEGG
- Reactome
- MSigDB
- …
- Previous studies
- Markers of a population of interest
- Targets of a transcription factor of interest
- DE genes from another analysis
Gene ontology
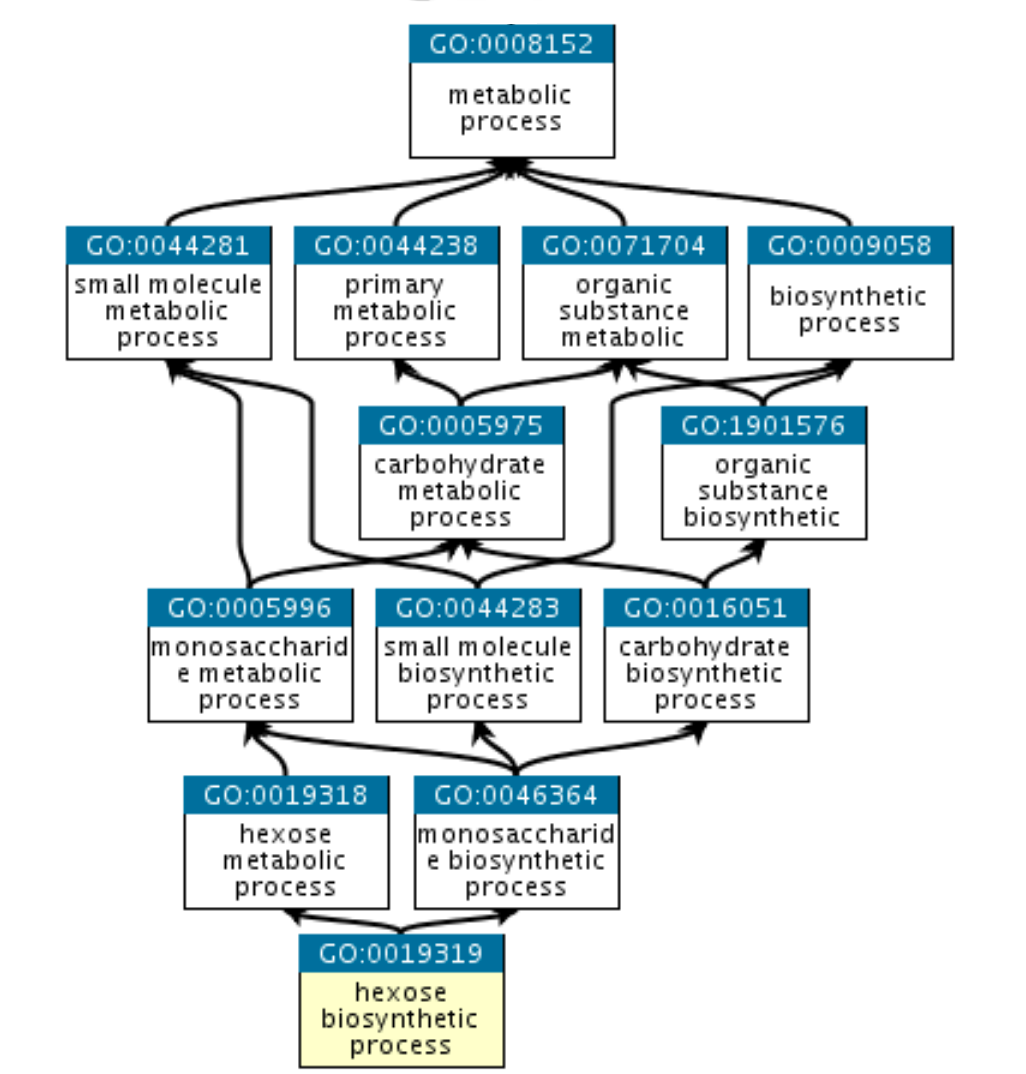

- Network graph, loosely hierarchical
- Three ontologies
- Biological process (e.g. Neutrophil Chemotaxis, Cell proliferation)
- Molecular Function (e.g. Histone acetylation, Phosphorylation)
- Cellular compartment (e.g. Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Plasma membrane)
- Genes can belong to multiple terms
Kegg

- Fewer and smaller ontology
- Highly curated
Overrepresentation analysis (ORA)
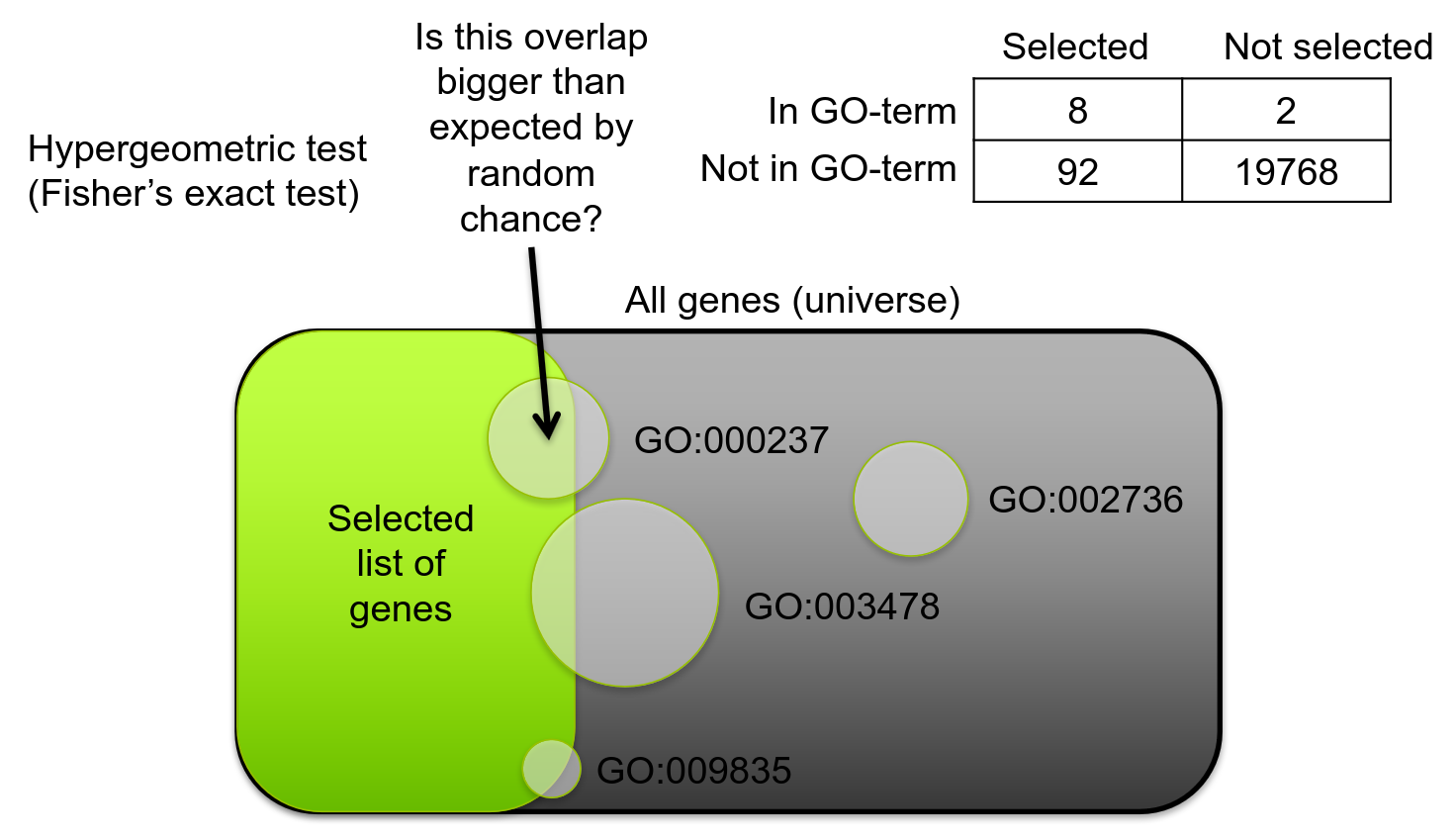
- Hypergeometric test (Fisher’s exact test)
Overrepresentation analysis (ORA)
- Background can be all genes or all genes expressed in your cell population
- Requires arbitrary cut-off
- Omits actual gene-level statistics
- Computationally fast
- Generally works for few genes with strong effects
Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA)

Subramanian et al. (2005)
Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA)
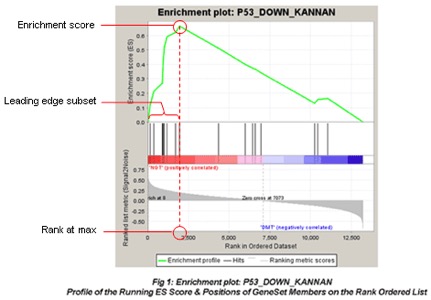
- Enrichment score (ES)
- Normalized enrichment score (NES)
- No need for cut-offs
- Takes gene-level stats into account
- More sensitive to subtle changes
Tools
Online
Code
Considerations
- Bias in curation - highly researched topics will be over-represented
- Gene set names can be misleading
- Specific vs general gene sets
- Multifunctional genes
- Translation of gene ids
- Databases change
- Curation is organism-specific
- Critical evaluation is required
References
Subramanian, A., Tamayo, P., Mootha, V. K., Mukherjee, S., Ebert, B. L., Gillette, M. A., Paulovich, A., Pomeroy, S. L., Golub, T. R., Lander, E. S., et al. (2005). Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 102(43), 15545–15550. https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.0506580102
Acknowledgements
Adapted from previous presentations by Leif Wigge, Paulo Czarnewski and Roy Francis.

