@HD VN:1.6 SO:coordinate
@SQ SN:LG4 LN:100000
@RG ID:SRR9309790 SM:PUN-Y-INJ PL:ILLUMINA
@PG ID:bwa PN:bwa VN:0.7.19-r1273 CL:bwa mem -R @RG\tID:SRR9309790\tSM:PUN-Y-INJ\tPL:ILLUMINA -p -t 30 -M tiny/ref/M_aurantiacus_v1_splitline_ordered.fasta -Read mapping
Mapping reads to a reference sequence
Per Unneberg
Sequence alignment maps reads to a reference
Aim of sequence alignment (read mapping) is to determine source in reference sequence. Some commonly used read mappers for resequencing are
- BWA, BWA-MEM (Li, 2013)
- Novoalign (https://www.novocraft.com/)
- Minimap2 (Li, 2018)
For a recent comprehensive comparison see Donato et al. (2021)
Alignments are stored in BAM format
Header information
Format: metadata record types prefixed with @, e.g., @RG is the read group
Alignments
SRR9309790.7750070 65 LG4 1 39 45S9M1I96M = 83782 83781 TGAACTATAGTCGATGGGACGAATACCCCCCTGAACTTGCGAAGGGGACAATTACCCCCCTCTGTTATGTTTCAGTCAATTTCATGTTTGATTTTTAGATTTTTAATTAATTATATATTTTTTGCAATTTGTAACCTCTTTAACCTTTATT AAFFFJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJAJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJFJJJJJJJJJJJFFJFJJJJJJJJJJFJJJJJJJJFJJJJJJJJJAJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJFA<FFJJ7FF SA:Z:LG4,83018,+,30M2I28M91S,37,5; MC:Z:12S10M2I123M4S MD:Z:16C28C59 PG:Z:MarkDuplicates RG:Z:SRR9309790 NM:i:3 MQ:i:50 AS:i:88 XS:i:70 ms:i:5185Some important columns: 1:QUERY, 3:REFERENCE, 4:POSITION, 5:MAPQ, 6:CIGAR. The CIGAR string compiles information on the alignment, such as match (M), soft clipping (S), and insertion to reference (I)
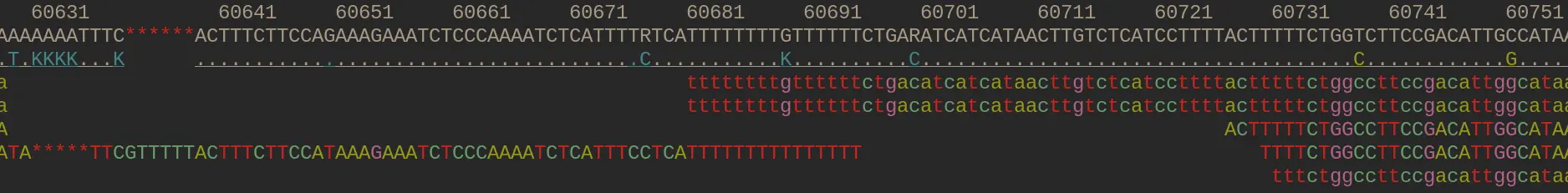
Mapped alignments can be viewed with samtools tview
LG4:30430
30431 30441 30451 30461 30471
CATTGGCAATGGCATCAGTTGAGCATCTTAGTACGAACTAAAAGCTGCGAAAAAATATTT
...............M............................................
...............A... ,,,,,,,,,,
...............A................. ,,,,,,,,,,
.............................................. ,,,,,,,,
..............................................
..............................................
...............A............................................
...............A............................................
,,,,,,,,,,,,a,,a,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,a,,a,,,,,,,,,,,,
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,a,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,a,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,a,,,,,aa,a,,,,,,,,,,,,
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,a,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
,,,,,,,,,,,,,a,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
LG4:30430
30431 30441 30451 30461 30471
CATTGGCAATGGCATCAGTTGAGCATCTTAGTACGAACTAAAAGCTGCGAAAAAATATTT
...............A............................................
,,,,,,, ..........................
...............A..... .....................
...............A...A.... .....................
...............A.........
...............A...........C.............
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,a,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,a,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
...............A............................................
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,a,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,a,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,a,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,a,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
...............A............................................
,,,g,,,,,,,a,,,a,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
.............A............................................
Aka pileup format. Forward (.) and backward (,) mapping reads. Mismatches shown as letters.
Potential error corrections and pitfalls
Instrument
- PCR duplication
- biased PCR amplification of DNA molecules
- remove with
picard MarkDuplicatesorsamtools rmdup - should not be removed for targeted sequencing
- systematic errors from sequencing machine
- employ Base Quality Score Recalibration (BQSR)
- con: time consuming and inflates file size
Reference
- quality of reference sequence!
- poor mapping to misassembled / missing reference
- repetitive sequence
- often collapsed in assemblies -> inflates read mapping depth
Bibliography
Donato, L., Scimone, C., Rinaldi, C., D’Angelo, R., & Sidoti, A. (2021). New evaluation methods of read mapping by 17 aligners on simulated and empirical NGS data: An updated comparison of DNA- and RNA-Seq data from Illumina and Ion Torrent technologies. Neural Computing and Applications, 33(22), 15669–15692. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06188-z
Li, H. (2013). Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv:1303.3997 [q-Bio]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1303.3997
Li, H. (2018). Minimap2: Pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics, 34(18), 3094–3100. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty191
Read mapping